What Are 2D Barcodes and How Do They Compare to 1D Barcodes?
Barcodes have been a crucial part of inventory management, product tracking, and retail operations for decades. While 1D barcodes (like the UPC codes on most products) have been the standard for years, 2D barcodes are quickly gaining popularity due to their ability to store more data in a smaller space.
So, what exactly are 2D barcodes, and how do they compare to traditional 1D barcodes? Let’s break down their differences, advantages, and why 2D barcodes are becoming the new standard across industries.
What Are 1D Barcodes?
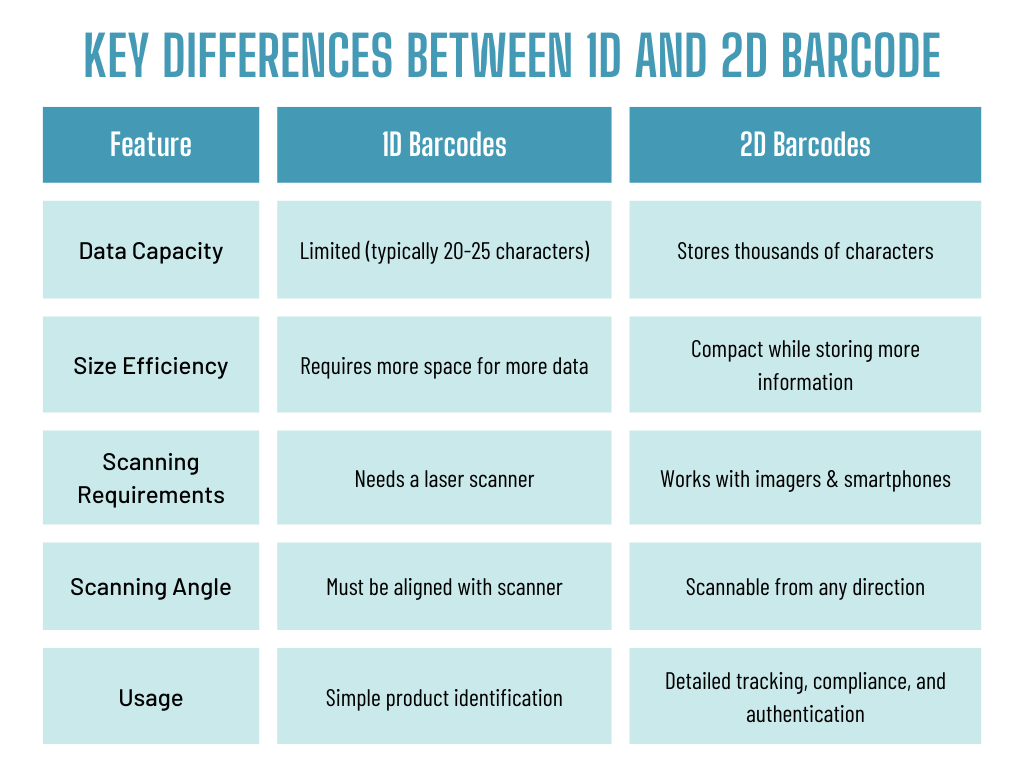
1D barcodes, also known as linear barcodes, are the traditional barcode format that consists of vertical black and white lines. These barcodes store information in a single horizontal direction and require a laser scanner or an imager to be read.
Common Examples of 1D Barcodes:
UPC (Universal Product Code) – Used for retail products.
EAN (European Article Number) – Common in international retail.
Code 128 & Code 39 – Used for shipping, logistics, and inventory tracking.
Limitations of 1D Barcodes:
✅Good for simple identification (SKUs, product pricing).
❌Limited data storage – Typically holds only a few characters.
❌Directional scanning required – Must be scanned from a specific angle.
❌Larger barcode size needed for more data – Takes up more space on labels.
What Are 2D Barcodes?
2D barcodes are a more advanced type of barcode that stores data both horizontally and vertically. This two-dimensional structure allows 2D barcodes to hold much more information without increasing in size. They can be scanned from any direction using imaging scanners or smartphone cameras.
Common Types of 2D Barcodes:
QR Codes – Widely used for marketing, payments, and website links.
Data Matrix Codes – Common in manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
GS1 DataMatrix – Used for pharmaceuticals, food traceability, and retail compliance.
Advantages of 2D Barcodes Over 1D Barcodes:
✅Stores more data – Can include product details, batch numbers, expiration dates, and even URLs.
✅Smaller size – Takes up less space on labels while holding more information.
✅Scannable from any angle – Eliminates the need for precise positioning.
✅Can be read with mobile devices – Smartphones and modern scanners can easily decode them.
Why Are 2D Barcodes Becoming the New Standard?
Industry Regulations & Compliance
Governments and organizations are pushing for item-level tracking, which requires 2D barcode adoption. Key regulations include:
GS1 Sunrise 2027 – Retailers are shifting to 2D barcodes for better product traceability.
FSMA 204 (Food Safety Modernization Act) – Requires detailed food tracking using GS1 DataMatrix codes.
DSCSA (Drug Supply Chain Security Act) – Pharmaceutical companies must use 2D barcodes for supply chain security.
Improved Supply Chain & Inventory Management
With 2D barcodes, businesses can:
✅Track individual items, not just product categories.
✅Reduce errors with better automation and real-time data updates.
✅Improve logistics with precise traceability from manufacturing to final sale.
Enhanced Customer Engagement
Brands are using QR codes to:
Offer product details and promotions.
Enable instant mobile payments.
Provide authentication against counterfeits.
Transitioning to 2D Barcodes: What You Need to Know
Check Your Scanners
Older laser scanners cannot read 2D codes.
Upgrade to 2D-compatible imaging scanners to ensure smooth adoption.
Update Label Printing Systems
Thermal label printers may need firmware updates or higher-resolution printing for clearer 2D barcodes.
Adapt Software for Item-Level Data
Traditional SKU-based tracking systems may require updates to handle serial numbers, batch tracking, and real-time attributes embedded in 2D codes.
Have questions about barcodes? Fill out the quick form below or contact us here and one of our barcode experts will be in touch with you!